Blended Learning "The Future of Education"
Education technology has granted an advanced place to educational institutions at all levels; it helps to achieve the desired reform in its educational systems with its various components. Using educational technology plays an essential role as it reduces the gap between social and economic realities and the outcomes of education and training systems by improving educational outputs and providing students and trainees with new knowledge and skills required in the age of knowledge economy. It also has a clear impact on expanding learning opportunities for a larger and more diverse people away from time or geographical boundaries.
Thus, blended learning, which includes a mix of direct face-to-face interactions and virtual interactions between students, instructors and learning resources, has emerged in a short time among the world's leading higher education institutions and placed at the top list of recent trends in higher education from 2012 to today. Blended learning offers opportunities for higher education institutions to achieve the learning outcomes needed to meet the needs of a modern world of a world dominated by globalization and technology. UNESCO emphasizes that blended learning is a valuable approach to help promote learning and achieve the fourth sustainable development goal known as Education 2030: ensuring quality and equitable education and lifelong learning opportunities in all forms of formal and non-formal education. The adoption of blended education is increasingly seen in higher education institutions, and researchers expect that blended learning will become the new "traditional model" (Ross & Gage, 2006) or the "new norm" in the introduction of higher education courses (Norberg, 2011).
Blended Learning Model at the Saudi Electronic University:
The Saudi Electronic University aims at providing high quality educational services in a learner-centered environment. The University has adopted a flexible model of blended learning that meets the needs of learners in the age of knowledge through a technological environment that utilizes ICTs, supports self and collaborative learning, and reduces learner's isolation in distance learning environment by combining direct education (face-to-face) both simultaneous and asynchronous, in an integrated model that combines its respective advantages.
The blended learning model at the Saudi Electronic University achieves the ideal balance between face-to-face and e-learning activities to provide students with a diverse and integrated learning experience that includes direct lectures, simultaneous virtual lectures, and synchronous/ asynchronous electronic activities on (Blackboard).
Global models of Blended Learning Implementation in Higher Education Institutions:
1. Supplemented Face-to-Face Model
This model is the closest to the traditional model and is based on the principle that direct education is the primary method, where the bulk of the course is delivered through face-to-face lectures while electronic elements are used in the classroom or remotely when needed to support students in order to complete certain tasks.


2. Enriched Virtual Model
In contrast to the supplemented face-to-face model, virtual distance learning is the foundation of this model. All expected activities occur in an electronic learning environment. These include peer-to-peer learning, reading, Communication and discussion in this form is conducted via electronic channels. Traditional classroom classes are not eliminated in this model. Additional lectures / sessions may be used on campus to provide additional support such as workshops.
3. Flex Model
In this model, learning is self-directed by students in an electronic environment where content and educational activities are provided. The student has a high degree of control over the learning process, where he / she can learn according to his / her own pace. Staff provides on-campus support and guidance, such as small study groups, individual lessons, etc., in a flexible framework that meets the needs of students as they progress in curriculum and learning content.
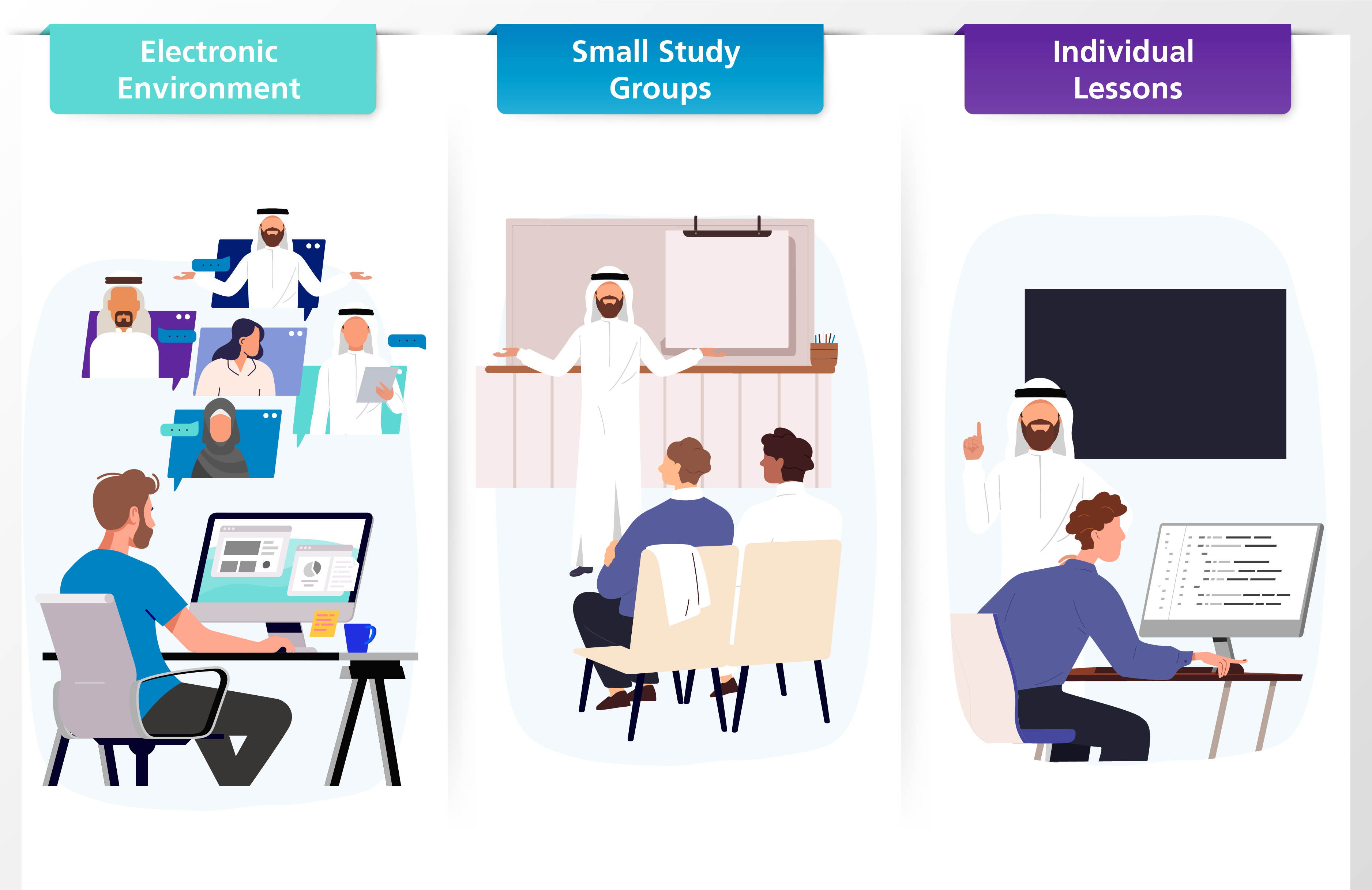
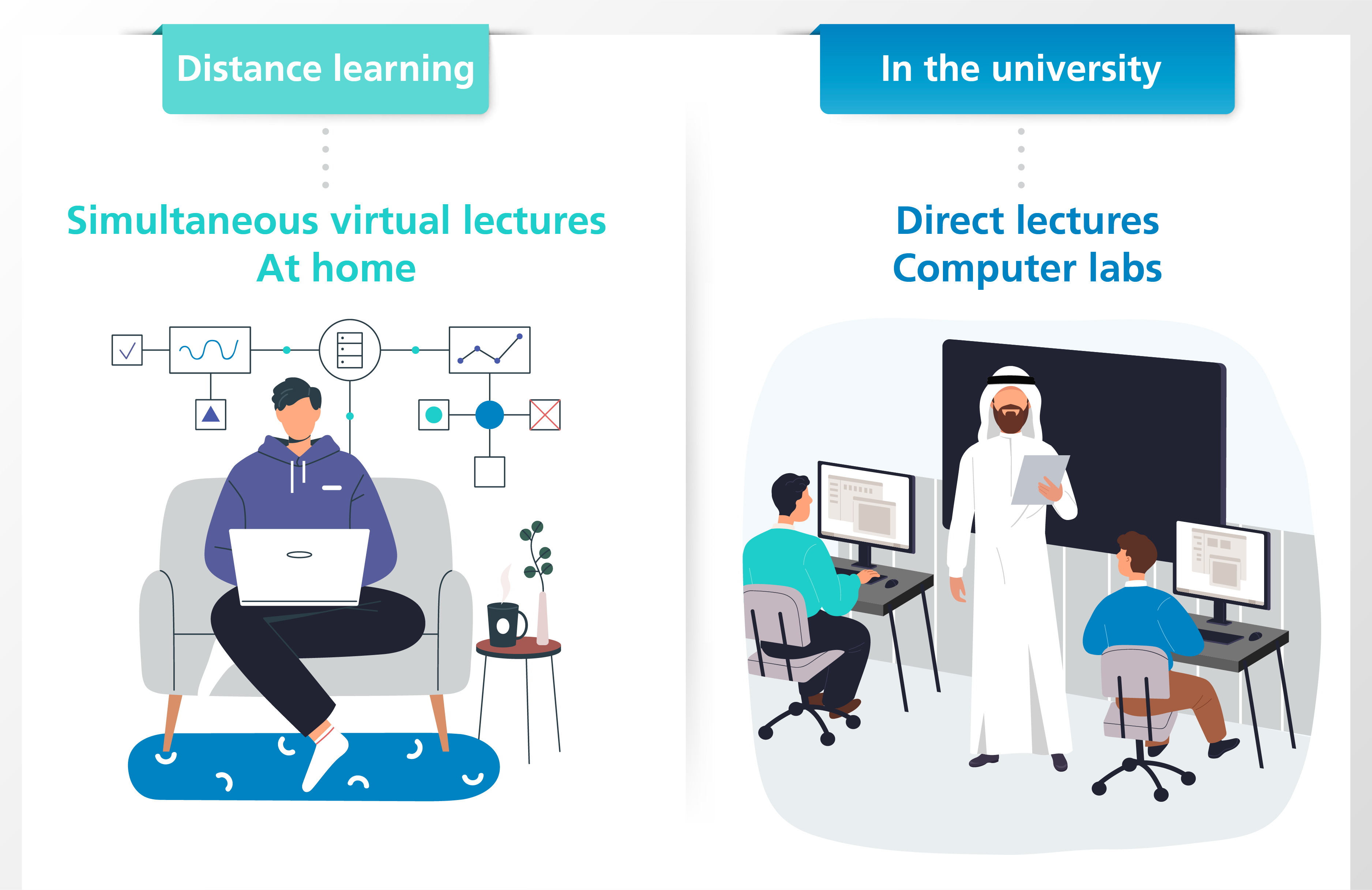
4. Selective Model A La Carte Model
This module enables students to register for courses offered online. In addition to the registration of traditional courses offered on campus, which gives students greater flexibility to design their schedules. A selective model is an appropriate option when the university can not offer specific learning opportunities or to study electives
5. Rotation Model
This model includes a table that compels students to rotate learning methods on a regular basis and may include students' rotation between face-to-face and online learning. The common feature of this pattern is regular scheduling, in which both online and direct learning - to face) sequentially; either to reinforce each other, or to widen the horizons of one or both. Several models have been formed from this model:
- Beginning and end model.
- Beginning middle and end model.
- Reverse class model.
- Week on / week off model.
- Inside-Out Blended Learning.
- Model Outside-In Blended Learning.
Benefits of Blended Learning
Enrich both the students educational experience and learning outcomes.
Achieve students' aspirations for optimal benefit of technology, as well as develop new skills that will qualify them for labor market (The Global Networked Environment).
Meet the individual's needs, learning style and personal agenda.
Motivate the development of self-learning skills.
Develop faculty members' skills and level of knowledge in order to transform and develop the teaching process.
Strengthen the links between the classroom and the real world.
Enhance the accessibility and flexibility of access to study resources and activities, especially for people with work, family or geographic difficulties.
Help to reduce the cost of delivering education and optimize the use of physical and virtual resources.
Increase the level of competition in building a new student market, thanks to innovation in the implementation of study programs